Although it can be very tough to live with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), symptoms frequently worsen when anxiety is present. Managing of both disorders depends on knowing whether anxiety is triggered by your IBS or vice versa. In order to control over your stomach and your anxiety, we’ll take you through the science behind IBS anxiety as well as tried-and-true dietary, lifestyle, and mental health techniques in this guide.Moreover,we will discuss coping tips for IBS Anxiety in daily life as well as will aware when to see a doctor or specialist.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a range of symptoms including abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits such as diarrhea or constipation. It is a chronic condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. One interesting aspect of IBS is its connection to anxiety, particularly in relation to the fear of certain foods triggering symptoms.
IBS and Anxiety:
IBS is a complex condition with multiple factors contributing to its development and exacerbation. Research suggests that there is a bidirectional relationship between IBS and anxiety. This means that IBS symptoms can trigger anxiety, and anxiety can worsen IBS symptoms. The exact mechanisms of this relationship are not fully understood, but several factors play a role:
- Brain-Gut Interaction: The gut and the brain are closely connected through the gut-brain axis. Stress and anxiety can influence gut function, leading to changes in motility and sensitivity, which are often seen in IBS.
- Hypervigilance: Anxiety can lead to heightened awareness of bodily sensations, including those related to digestion. This hypersensitivity can make IBS symptoms feel more intense and distressing.
- Microbiota: The gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, can be affected by stress and anxiety. Imbalances in the microbiota have been linked to IBS symptoms.
Managing IBS
Managing IBS involves a combination of medical treatments, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan. Here are some strategies commonly used to manage IBS:
- Dietary Modifications: Identifying trigger foods and making dietary changes is crucial for managing IBS. Common trigger foods include high-fat foods, dairy products, caffeine, artificial sweeteners, and certain types of carbohydrates (FODMAPs). A low FODMAP diet, under the guidance of a registered dietitian, may help alleviate symptoms.
- Stress Reduction: Managing stress and anxiety can have a positive impact on IBS symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve gut function.
- Medications: Depending on the symptoms and their severity, healthcare providers may prescribe medications such as antispasmodics, laxatives, anti-diarrheal drugs, and even low-dose antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications.
- Probiotics: Some individuals with IBS find relief from symptoms by taking certain strains of probiotics, which can help restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate bowel function, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It has been shown to be effective in managing both IBS symptoms and anxiety.
The Fear of Food and Anxiety:
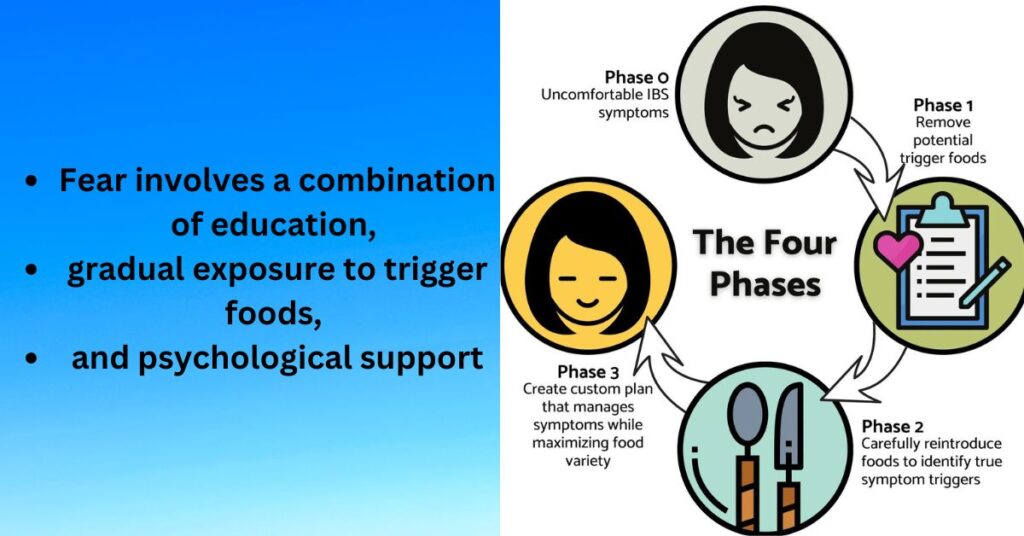
For some individuals with IBS, a fear of triggering symptoms through specific foods can lead to a cycle of anxiety and avoidance. This fear can result in restrictive eating patterns, which may further exacerbate the gut-brain interaction. Addressing this fear involves a combination of education, gradual exposure to trigger foods, and psychological support. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, as well as therapy aimed at addressing food-related anxieties, can be helpful in breaking this cycle.
Coping Tips for Everyday IBS Anxiety
- Prepare safe meals in advance.
- Use calming tools like breathing apps or music before meals.
- Plan bathroom access when traveling.
- Speak openly with friends or coworkers about your condition (if you’re comfortable).
- Practice self-compassion; it’s not “in your head,” and you’re not alone.
When to See a Doctor or Specialist
- If symptoms are severe, worsening, or new.
- If anxiety is interfering with daily life.Must visit gastroenterologists, psychologists, and dietitians.
Conclusion
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a multifaceted condition that often intertwines with anxiety. Understanding the relationship between IBS and anxiety is crucial for effective management. By implementing a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, dietary modifications, and stress reduction, and psychological support, individuals with IBS can achieve better symptom control and improved quality of life. If you or someone you know is struggling with IBS and anxiety, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and mental health experts is recommended.





